🤯 INCRÍVEL: “It’s Called The Mammalian Dive Reflex”: 50 Facts About The Human Body That Sound Fake But Aren’t 😲
One of the biggest mistakes you can make in life is believing that you know everything there is to know. Even if you’re highly educated and brag about how brainy you are, there’s always—always!—something new to learn. If you keep your curiosity alive and well, and stay humble, you might fill in some of the biggest knowledge gaps you didn’t even know you had.
Today, we’re featuring some of the strangest, most interesting, and frankly mind-blowing facts about the human body that internet users shared in a couple of awesome online threads. Scroll down to check them out and, hopefully, learn something new.
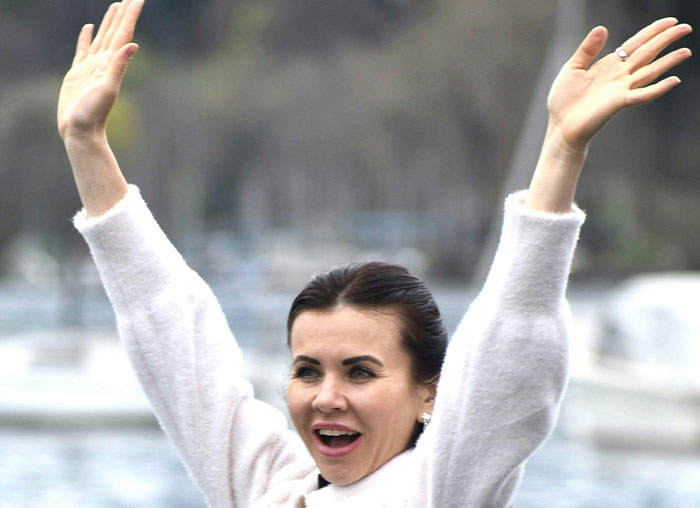
 When blind people win a competition they raise their arms in a victory salute, in spite of never seeing that done before. It seems to be inherent, and some suggest that it shows our connection to primates. Gorillas raise their arms to show dominance over others.
When blind people win a competition they raise their arms in a victory salute, in spite of never seeing that done before. It seems to be inherent, and some suggest that it shows our connection to primates. Gorillas raise their arms to show dominance over others.
As T. Alexander Puutio, Ph.D., who teaches organizational performance and leadership at Harvard and Columbia, stresses in a post on Psychology Today, there are many benefits of staying curious as you age.
For example, older adults who “remain intellectually adventurous maintain better cognitive functioning and enjoy lower dementia risk than their less curious peers.”
What’s more, novel experiences stretch your perception of time, so you feel like you live longer and more vividly.
Not only that, but curiosity also predicts “greater meaning in life and higher psychological well-being across cultures.”
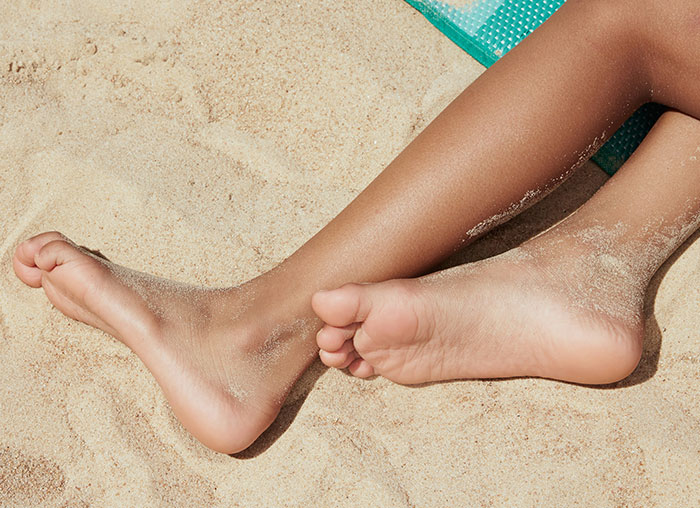 * there are ~250,000 sweat glands in a pair of feet.
* there are ~250,000 sweat glands in a pair of feet.
* feet perspire more than any other part of the body
* a pair of feet produce a 1/2 pint of sweat a day or a full pint if one wears non-breatheable footwear.
Meanwhile, Leon F. Seltzer, Ph.D., the author of ‘Paradoxical Strategies in Psychotherapy,’ notes that curiosity improves cognitive functioning while also helping your mind work more logically and efficiently.
Moreover, staying curious about the world can also boost your confidence, self-esteem, sense of pride, purpose, and life direction.
“Virtually all of us are endowed with a sense of adventure. And so we’re attracted to, and motivated to engage in, what’s novel or new. That’s how, ongoingly, we’re able to take in what previously we weren’t conscious of. As a result, we start to recognize what may still remain outside our awareness, which can incite us to continue our pursuit of knowledge and understanding on an ever-deepening level,” Seltzer writes on Psychology Today.
“Furthermore, as we’re driven to indefinitely expand our knowledge, we become interested in related questions not previously considered. And that prompts us to seek out fresh experiences to obtain information that now draws our curiosity. Needless to say, this well-nigh perpetual venture serves to enrich our lives and make them more meaningful.”
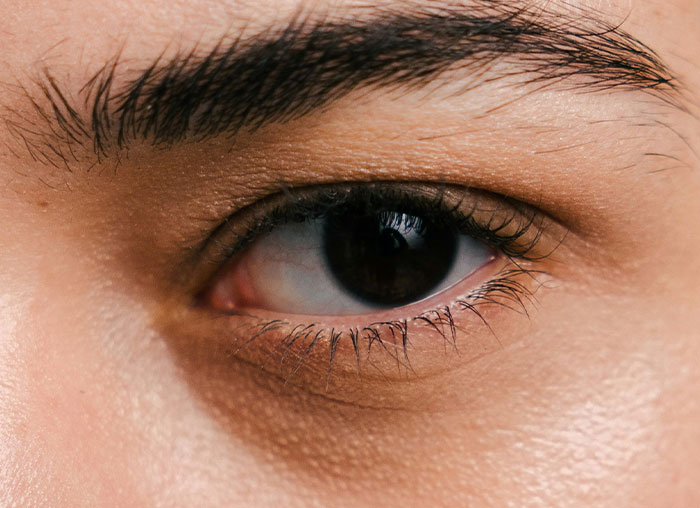 The part of your eye where the optic nerve exits is what gives you a blind spot, because there are no photoreceptors at that part of the retina. It’s a bit of a design flaw, but luckily, the spot is “filled in” by your brain so, you don’t notice.
The part of your eye where the optic nerve exits is what gives you a blind spot, because there are no photoreceptors at that part of the retina. It’s a bit of a design flaw, but luckily, the spot is “filled in” by your brain so, you don’t notice.
When you’ve read through all of these intriguing facts, we’d like to hear from you, Pandas. Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments at the very bottom of this post.
How do you continue to stay curious about the world, no matter how many responsibilities and other things you have going on in your life? What are the weirdest things you’ve learned about the human body that sound fake but are completely true? What do you do to accept the world for what it is, not what you think it should be? Tell us all about it.
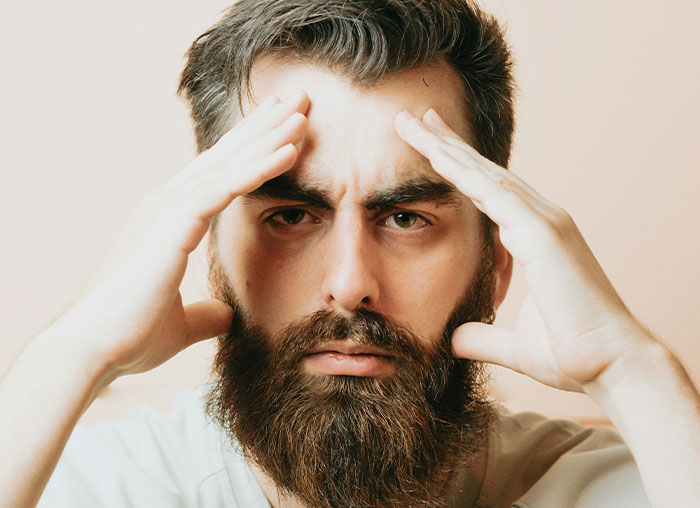 Your memories are not concrete. Every time you think about a memory it becomes volatile and can be changed. There was an experiment where people were told that they had committed a major crime earlier in their life. This was of course false, but after being told repeatedly for weeks the people became completely convinced that the crime really happened.
Your memories are not concrete. Every time you think about a memory it becomes volatile and can be changed. There was an experiment where people were told that they had committed a major crime earlier in their life. This was of course false, but after being told repeatedly for weeks the people became completely convinced that the crime really happened.
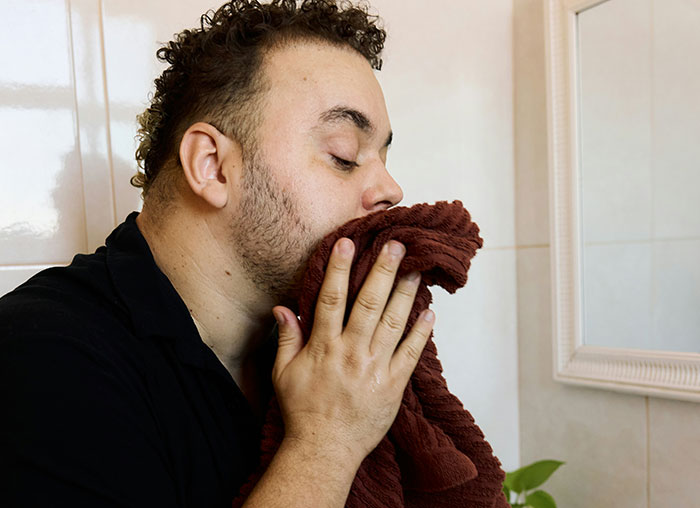 Right before you vomit your mouth fills with quite a bit of saliva, this normally happens like 30-45 seconds before you vomit. It does this to help protect your mouth from the acids in the vomit. It’s also a good indicator that you are going to vomit. So if that happens to you find the nearest toilet, bush, or garbage can.
Right before you vomit your mouth fills with quite a bit of saliva, this normally happens like 30-45 seconds before you vomit. It does this to help protect your mouth from the acids in the vomit. It’s also a good indicator that you are going to vomit. So if that happens to you find the nearest toilet, bush, or garbage can.
 * extremely efficient legs, we can walk all day, but a horse or a wolf tires out much earlier.
* extremely efficient legs, we can walk all day, but a horse or a wolf tires out much earlier.
* resistance to shock, losing a body-part isn’t a completely lethal, as with other creatures.
* hyperactive scar tissue, we regenerate faster than other creatures.
* Mega-fauna, we are in the group mega-fauna, which means we are one of the largest creatures on the Earth.
 The appendix has a purpose and is not just a genetic remnant. It holds onto bacteria as a reserve for your digestive track incase your system is rapidly flushed (toxins, new bacteria, swift kick to your gooch). In a sense, its a lifeboat for probiotic (if your system was healthy and stable before it hit the fan).
The appendix has a purpose and is not just a genetic remnant. It holds onto bacteria as a reserve for your digestive track incase your system is rapidly flushed (toxins, new bacteria, swift kick to your gooch). In a sense, its a lifeboat for probiotic (if your system was healthy and stable before it hit the fan).
 Dunno if this counts exactly but coconut water can be used as a temporary replacement for blood plasma. Yaknow, like, for emergency surgery on a stylised desert island?
Dunno if this counts exactly but coconut water can be used as a temporary replacement for blood plasma. Yaknow, like, for emergency surgery on a stylised desert island?
 If you held the pancreas in your hand it would dribble through your fingers because it has the viscosity of snot. That’s why pancreatic cancer is pretty much impossible to operate on.
If you held the pancreas in your hand it would dribble through your fingers because it has the viscosity of snot. That’s why pancreatic cancer is pretty much impossible to operate on.
 If your second toe is longer than your big toe, it is called Morton’s foot.
If your second toe is longer than your big toe, it is called Morton’s foot.
No Olympic sprinter has ever had a Morton’s foot (instead conforming to the standard downhill toes).
However, statues from Ancient Greece (as well as later Roman statues, Michelangelo’s David, Venus de Milo, Da Vinci’s Vitruvian Man and the Statue of Liberty) all portray Mortons feet as it was considered an ideal of beauty.
 There is no animal in the Animal Kingdom that can outrun a human in a distance race.
There is no animal in the Animal Kingdom that can outrun a human in a distance race.
Many animals can run faster that we do, but as far as distance goes we are unmatched.
Our ancestors used to practice persistance hunting.
“Persistence hunting is believed to have been one of the earliest hunting strategies used by humans.”.
 That females are born with ~2 million eggs already in their ovaries, although that’s down from a peak of 6 to 7 million while in the womb. They lose eggs over time naturally, and by the time they hit puberty they’re down to ~300,000.
That females are born with ~2 million eggs already in their ovaries, although that’s down from a peak of 6 to 7 million while in the womb. They lose eggs over time naturally, and by the time they hit puberty they’re down to ~300,000.
Still debate on whether or not they create new eggs in their life-time or if what they’re born with are all they’ll ever have, they’re still doing studies to try to figure this one out.
 There’s something called “placebo sleep”–if you trick your brain into thinking you got a good night’s sleep you will become convinced you got a good night’s sleep.
There’s something called “placebo sleep”–if you trick your brain into thinking you got a good night’s sleep you will become convinced you got a good night’s sleep.
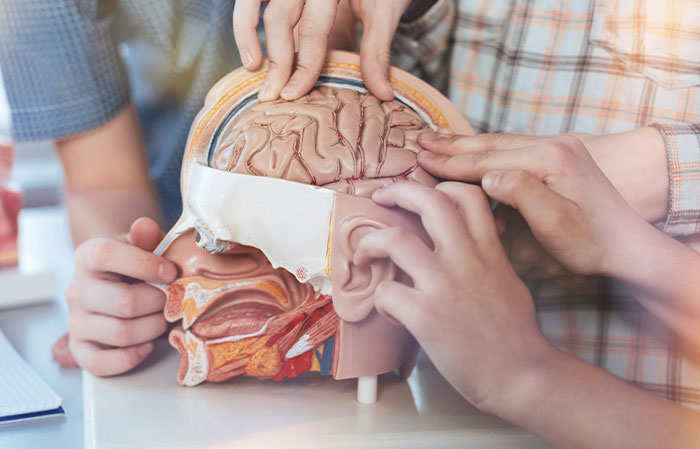 That we are all so different on the inside.
That we are all so different on the inside.
I assumed we were all cookie-cutter, like the anatomy posters. Then, I went to a cadaver lab, for school.
I saw a body with a bicep with 3 heads (making it a tricep) and 2 heads on the tricep (making it a bicep)
Some people have extra organs (extra kidneys).
I had just assumed… (it also puts evolution into a more real context).
 Human babies are so helpless when they’re first born because they’re not done developing yet. It has been hypothesized that when humans evolved to walk on two legs, one of the consequences was the narrowing of the birth canal, meaning that babies need to be born earlier or else their heads would be too large to pass through. In theory, a human gestational period would ideally be between 18-21 months!
Human babies are so helpless when they’re first born because they’re not done developing yet. It has been hypothesized that when humans evolved to walk on two legs, one of the consequences was the narrowing of the birth canal, meaning that babies need to be born earlier or else their heads would be too large to pass through. In theory, a human gestational period would ideally be between 18-21 months!
The skin on your elbow is called a Wenis.
Took anatomy in university, the biggest thing that stuck out to me was the wrist/hand.
There is so much packed through the wrist and into the hand it’s insane. You got muscles, tendons, bones, veins, arteries, and nerves, all bottle necked through about a 2” x 1” opening.
And not only that, but think about how strong your hands are, and yet how delicate and precise they can be.
It’s cray cray.
The 52 bones in your feet make up one quarter of all the bones in your body. When they are out of alignment, so is the rest of your body.
All the processes that happen in your body happen in complete darkness.
When people think about bodily processes they think of images of pink and red things moving around in a well-lit environment. In reality it’s all pitch black.
The average human heart pumps about 7600 liters (2000 gallons) of blood every day.
Your heart does a lot of work. Take care of it.
A woman’s breast milk adapts to her infant’s needs based on its saliva. If the baby is sick, mom will produce more antibodies in her milk.
You are at your tallest each day as soon as you wake up in the morning.
I’m pretty sure alot of people know about the whole ‘eyes take in an upside down image and the brain flips it’ thing, but if you wear glasses that flip what you see upside down your brain will eventually adjust and flip how you perceive it the “right” way up, this means that when you take the glasses off you’ll see upside down naturally until your brain readjusts again.
It’s funny but the nail on the middle finger grows faster than the rest. And the nail on the middle finger of the leading hand is generally a champion in terms of growth rate)
We still don’t know why but the growth speed of the nail is somehow connected with the length of the finger, so that fingernails on long fingers grow faster than all, and the slowest on short ones.
There is a natual chimerism present in every woman’s body.
Early in foetal development every cell has to decide for itself which X-chromosome it will use. Once that decision is made it sticks everytime the cell divides. So you get clumps/stripes of cells that share the same x-chromosome next to stripes/clumps that have the other chromosome active.
Tilapia skin is close enough to our skin that it can be used to paper over burns and let them heal faster.
Also, our immune systems are similar enough to pigs’ that they are the (non-primate) animal that transmit diseases the most easily to us, which is likely why many early religions banned pigs as dirty.
No matter how warm or hot the outside cold air is our nose changes it to 98F immediately breathing it in.
That muscles can exert a lot more force than they actually do. They aren’t used to there full potential all the time because it would destroy the muscle.
When you get an adrenaline rush you are able to tap in to more of your muscles and become significantly stronger.
During the average person’s life, they will produce enough saliva to fill two swimming pools. Now I know where Mark Spitz got his name from.
The acid in your stomach could burn your skin! I always thought that was pretty interesting, and reminds me of the scene in Alien, where the alien blood burns everything.
That the brain operates on the same amount of power as a 10-watt lightbulb.
📢 Gostou da notícia? Compartilhe com os amigos!
Este artigo é uma tradução automática de uma fonte original. Para ler o conteúdo na íntegra: Clique aqui.

